GPUs have changed the face of deep learning and made what once took weeks happen in just hours. While most people think of graphics cards as tools for gaming or videos, these processors actually hold the key to modern artificial intelligence. A single high-end GPU can run thousands of computations at the same time, slashing machine learning training times by as much as 90 percent. That speed is just the start—what matters most is how this technology has taken advanced AI out of the research lab and put it into real-world applications everyone depends on today.
GPUs have transformed deep learning by providing unprecedented computational power for complex neural network training and inference tasks. Unlike traditional central processing units (CPUs), GPUs excel at parallel processing, making them ideal for the massive matrix calculations required in machine learning algorithms.
The fundamental advantage of GPUs in deep learning stems from their unique architecture. Where CPUs are designed to handle sequential tasks efficiently, GPUs contain thousands of smaller, more specialized cores capable of performing multiple calculations simultaneously. This parallel processing capability allows GPUs to dramatically accelerate training times for complex neural networks.
Typical deep learning workloads involve millions of mathematical operations happening concurrently. Our guide on AI computing infrastructure explains how this architecture translates into real-world performance gains. Modern GPUs can process thousands of computational threads simultaneously, reducing training times from weeks to hours or even minutes.
Deep learning models rely on complex tensor operations and matrix multiplications. According to research from Stanford University, GPUs are specifically engineered to handle these computations with exceptional efficiency. The architecture allows for:
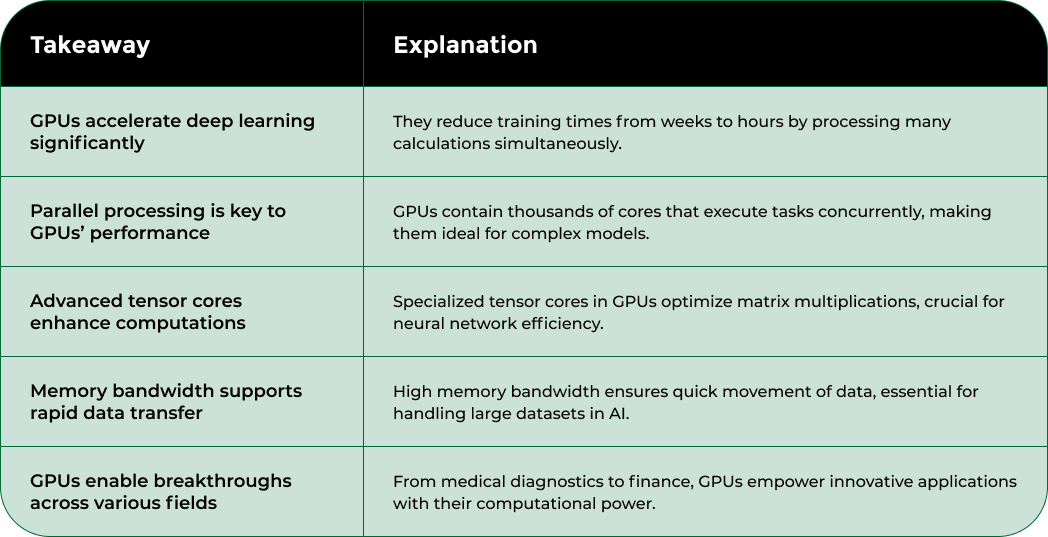
By enabling rapid, simultaneous computations, GPUs have become the cornerstone of modern deep learning research and industrial applications, powering everything from image recognition systems to natural language processing models.
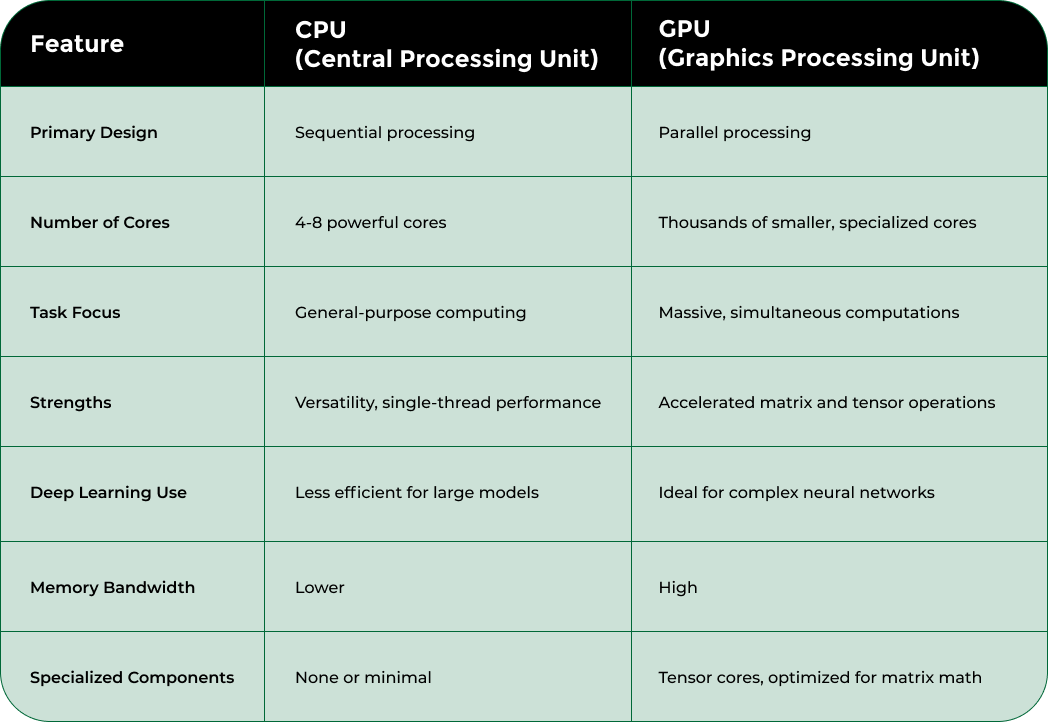
The table below highlights the main architectural and operational differences between CPUs and GPUs for deep learning, making it easier to understand why GPUs offer superior performance for these tasks.
Machine learning performance hinges critically on computational speed and efficiency, areas where GPUs have revolutionized computational capabilities. These specialized processors represent a quantum leap in how complex algorithms are executed, enabling breakthroughs across artificial intelligence domains.
The core significance of GPUs in machine learning lies in their ability to dramatically reduce computational time. Traditional computing models struggled with the immense mathematical complexity of neural networks, but GPUs transform this challenge by enabling massive parallel processing. A single high-performance GPU can execute thousands of computational threads simultaneously, effectively condensing computational timelines from weeks to mere hours.
AI applications in financial services demonstrate how this acceleration translates into practical technological advantages. By distributing computational workloads across numerous specialized cores, GPUs eliminate sequential processing bottlenecks that traditionally hindered machine learning model training.
Modern machine learning models demand exponential computational resources. According to research published by MIT, GPU performance metrics reveal extraordinary improvements in deep learning training efficiency:
These technological innovations mean machine learning researchers and practitioners can develop increasingly sophisticated models without being constrained by computational limitations. GPUs have transformed machine learning from a theoretical discipline into a practical, rapidly evolving field of technological innovation.
Graphics Processing Units represent an extraordinary leap in computational architecture, fundamentally reimagining how complex mathematical operations are processed. Unlike traditional CPUs designed for sequential computing, GPUs are engineered to handle thousands of calculations simultaneously, making them revolutionary for machine learning and high-performance computing tasks.
The defining characteristic of GPU technology is its massively parallel processing design. Where a typical CPU might have 4-8 powerful cores optimized for sequential tasks, modern GPUs contain thousands of smaller, highly efficient cores specifically designed to execute multiple computations concurrently.
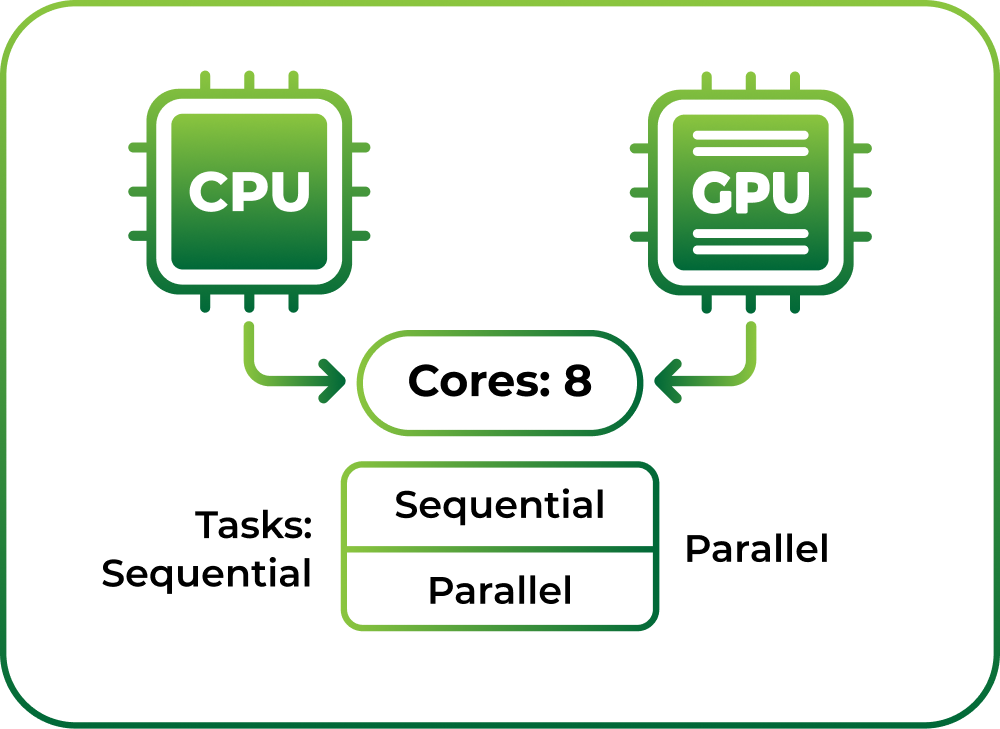
This architectural difference enables GPUs to break down complex problems into smaller, manageable computational threads that can be processed in parallel.
Learn more about AI computing infrastructure to understand how this parallel processing translates into real-world computational advantages. Each GPU core can independently handle specific mathematical operations, allowing for unprecedented computational efficiency.
According to research from the University of Virginia, GPU performance is characterized by several critical technical attributes:
These components work in concert to transform how computational problems are solved. By distributing workloads across numerous cores, GPUs can complete complex mathematical operations exponentially faster than traditional computing architectures, making them indispensable for machine learning, scientific simulations, and advanced data processing tasks.
Deep learning acceleration represents a critical technological frontier where GPUs transform computational capabilities, enabling unprecedented performance in complex machine learning tasks. By reimagining computational architecture, GPUs have become the backbone of modern artificial intelligence research and industrial applications.
At the heart of GPU acceleration lies the principle of massive parallel processing. Unlike traditional computing models that process tasks sequentially, GPUs distribute computational workloads across thousands of specialized cores simultaneously. This architectural innovation allows for exponential increases in computational speed, dramatically reducing the time required to train sophisticated neural networks.
Our comprehensive guide to AI computing infrastructure provides deeper insights into how these technological advancements translate into real-world performance gains. The ability to execute thousands of mathematical operations concurrently represents a quantum leap in computational efficiency.
According to research from Cornell University, GPU acceleration in deep learning encompasses several sophisticated techniques:
These advanced techniques collectively enable GPUs to handle the immense computational complexity of modern deep learning models, transforming theoretical machine learning concepts into practical, scalable technological solutions.
GPUs have transcended their original graphics rendering purpose to become fundamental technology driving innovation across multiple scientific and industrial domains. Their unprecedented computational capabilities enable researchers and enterprises to solve complex problems that were previously considered computationally intractable.
Modern GPUs serve as critical computational engines across diverse fields, processing massive datasets and executing intricate algorithms with remarkable efficiency. From climate modeling to medical imaging, these specialized processors have become indispensable tools for pushing technological boundaries. Their ability to perform thousands of simultaneous calculations makes them uniquely suited for handling the computational demands of advanced artificial intelligence and data science applications.
Explore digital transformation strategies to understand how GPU technologies are reshaping technological landscapes across industries. The computational power of GPUs enables breakthroughs that were unimaginable just a decade ago.
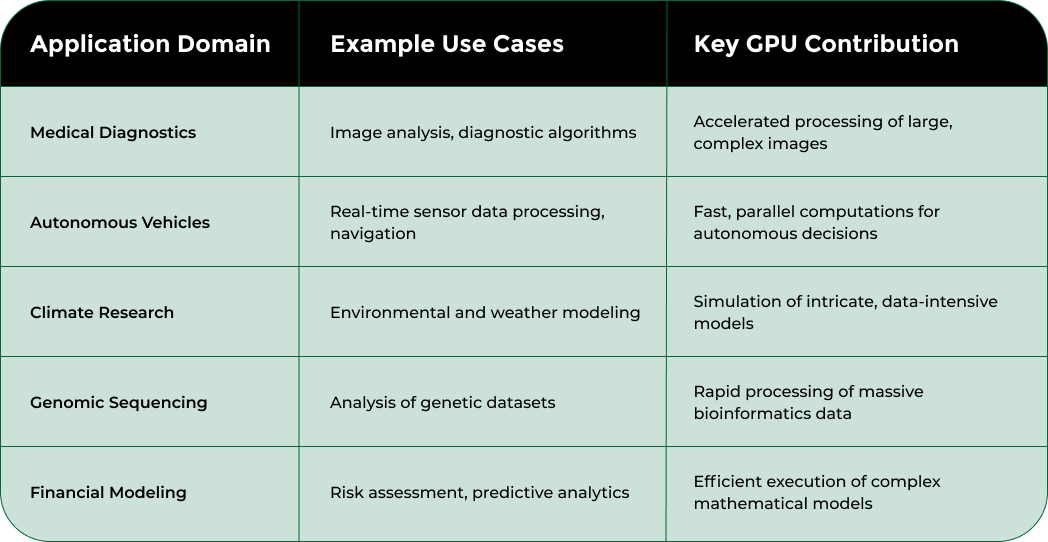
According to research published in computational science journals, GPU applications span several critical domains:
These applications demonstrate how GPUs have evolved from specialized graphics processors to fundamental technological infrastructure enabling groundbreaking scientific and industrial innovations.
This table summarizes major real-world application domains where GPUs have enabled breakthroughs in artificial intelligence and data science through their powerful computational abilities.

If you found yourself concerned by the technical bottlenecks and long training times highlighted in our guide “What is GPU in Deep Learning? A Comprehensive Guide,” you are not alone. Many organizations discover that even the best research and model ideas are limited by hardware shortages slow scalability or unreliable infrastructure. With modern deep learning requiring massive matrix computations and advanced tensor core performance, the need for high-throughput GPU solutions has never been more urgent.
Stop letting outdated or insufficient infrastructure block your progress. Visit https://nodestream.blockwaresolutions.com for immediate access to AI-ready GPU servers and verified HPC assets tailored for your actual workloads. Buy, sell, or customize solutions with full enterprise support and transparent logistics all in one place. Explore our AI computing infrastructure guide or connect directly with our platform to secure the power and flexibility you need for your next breakthrough. Act now to move ahead of the technology curve.
A GPU, or Graphics Processing Unit, is a specialized processor that excels in parallel processing, making it ideal for handling the complex mathematical calculations involved in deep learning and neural networks.
GPUs accelerate training by performing thousands of calculations simultaneously, reducing the time required to train complex neural networks from weeks to hours or even minutes.
GPUs offer massive parallelization, high memory bandwidth, and specialized cores for tensor operations, which allows for significantly faster processing of complex algorithms compared to traditional CPUs designed for sequential tasks.
Yes, GPUs are widely used in various fields such as medical diagnostics, climate research, autonomous vehicles, and genomic sequencing due to their powerful computational capabilities.